Pragmatic language, an essential aspect of human communication, enables us to convey our thoughts and intentions effectively in different social contexts. It encompasses the ability to interpret nonverbal cues, make inferences, and adapt our language to the situation and audience.
Understanding pragmatic language is crucial for fostering meaningful and successful interactions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of pragmatic language, exploring its components, developmental stages, and the impact of cultural factors. We will also discuss common disorders associated with pragmatic language and explore evidence-based intervention strategies to address these challenges.
Defining Pragmatic Language
Pragmatic language is the ability to understand and use language in a way that is appropriate for the context. It involves understanding the implied meaning of words and phrases, as well as the social and cultural rules that govern communication.
Pragmatic language skills are essential for effective communication. They allow us to communicate our thoughts and feelings in a way that is understood by others, and to interpret the messages of others accurately.
Examples of Pragmatic Language
- Using the appropriate tone of voice for the situation.
- Making eye contact when speaking to someone.
- Using body language to convey meaning.
- Understanding the meaning of sarcasm.
- Interpreting the intent of a speaker.
Components of Pragmatic Language
Pragmatic language encompasses several key components that interact to facilitate effective communication. These components include context, inference, and social cues, each playing a crucial role in conveying meaning beyond the literal words spoken.
Context
Context refers to the surrounding environment, including the physical setting, social situation, and cultural norms, that influences the interpretation of language. It provides a framework for understanding the speaker’s intent, tone, and the significance of their words.
Inference
Inference involves drawing conclusions and making assumptions based on the information provided. It allows listeners to fill in gaps in the conversation and understand the speaker’s implied meaning. Inference relies on the listener’s knowledge, experience, and cultural background.
Social Cues, Pragmatic language
Social cues are non-verbal signals, such as facial expressions, gestures, and body language, that provide additional information about the speaker’s intentions and emotions. These cues can reinforce, contradict, or modify the spoken words, helping listeners to interpret the message accurately.
Development of Pragmatic Language
The development of pragmatic language is a complex and gradual process that typically begins in infancy and continues throughout childhood and adolescence. During this time, children learn how to use language appropriately in different social contexts, how to understand the intentions of others, and how to negotiate meaning in conversations.
The typical developmental stages of pragmatic language acquisition include:
- Infancy (0-12 months):Prelinguistic communication, such as crying, cooing, and babbling, is used to express basic needs and emotions.
- Toddlerhood (1-3 years):Children begin to use single words and short phrases to communicate. They also start to understand simple questions and commands.
- Preschool (3-5 years):Children’s language skills develop rapidly. They begin to use more complex sentences, ask questions, and tell stories. They also start to understand the importance of context and tone of voice.
- School age (6-12 years):Children continue to develop their pragmatic language skills. They learn how to use language effectively in different social situations, such as at school, with friends, and with adults.
- Adolescence (13-18 years):Adolescents continue to refine their pragmatic language skills. They learn how to use language to express their own opinions and ideas, and to negotiate and resolve conflicts.
The development of pragmatic language skills is influenced by a number of factors, including:
- Cognitive development:Children’s cognitive development, such as their ability to understand and reason, plays a role in their ability to learn and use pragmatic language skills.
- Language development:Children’s overall language development, such as their vocabulary and grammar skills, is also important for the development of pragmatic language skills.
- Social development:Children’s social development, such as their ability to interact with others and understand social cues, is essential for the development of pragmatic language skills.
- Environmental factors:Children’s environment, such as the language they are exposed to and the opportunities they have to interact with others, can also influence the development of pragmatic language skills.
Pragmatic Language Disorders
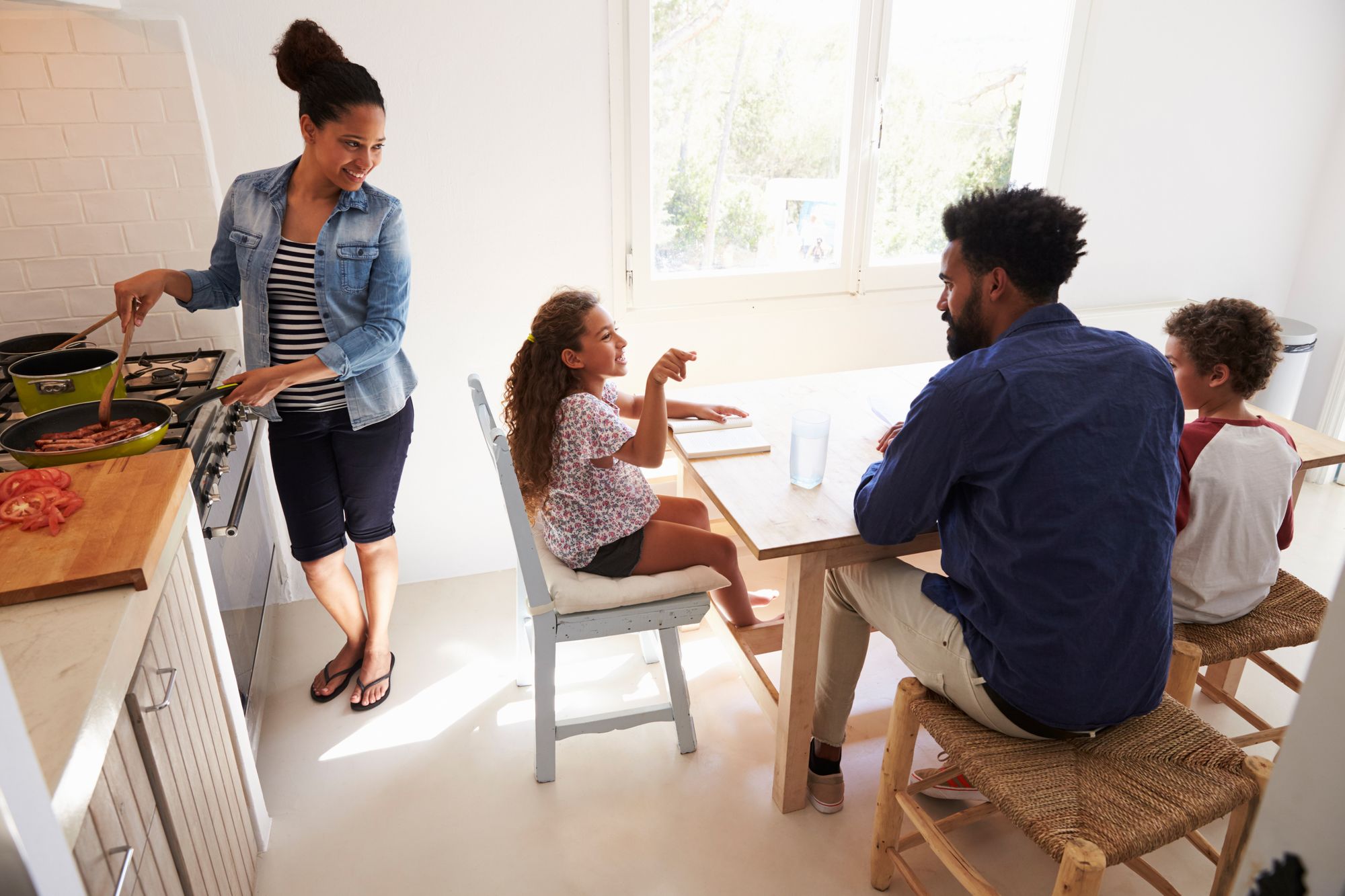

Pragmatic language disorders are communication difficulties that affect a person’s ability to understand and use language in social situations. These disorders can range from mild to severe and can impact a person’s ability to communicate effectively in a variety of settings.
Common Types of Pragmatic Language Disorders
There are several different types of pragmatic language disorders, including:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): ASD is a developmental disorder that affects a person’s ability to communicate and interact with others. People with ASD may have difficulty understanding social cues, interpreting nonverbal communication, and engaging in reciprocal conversation.
- Social (Pragmatic) Communication Disorder: This disorder is characterized by difficulties in using language for social purposes, such as greeting others, making requests, and maintaining conversations. People with this disorder may also have trouble understanding the intentions of others and may appear to be aloof or uninterested in social interactions.
- Specific Language Impairment (SLI): SLI is a language disorder that affects a person’s ability to understand and use language. People with SLI may have difficulty with grammar, vocabulary, and pragmatics.
Assessment and Intervention for Pragmatic Language Disorders
Assessment of Pragmatic Language Skills
Assessing pragmatic language skills involves evaluating an individual’s ability to use language appropriately in social situations. Methods used include:
- Conversational analysis:Observing and analyzing real-world conversations to assess social interaction and communication patterns.
- Pragmatic language tests:Standardized assessments designed to measure specific pragmatic skills, such as understanding and using social cues.
- Questionnaires and interviews:Collecting information from individuals, parents, or teachers about communication behavior and social interactions.
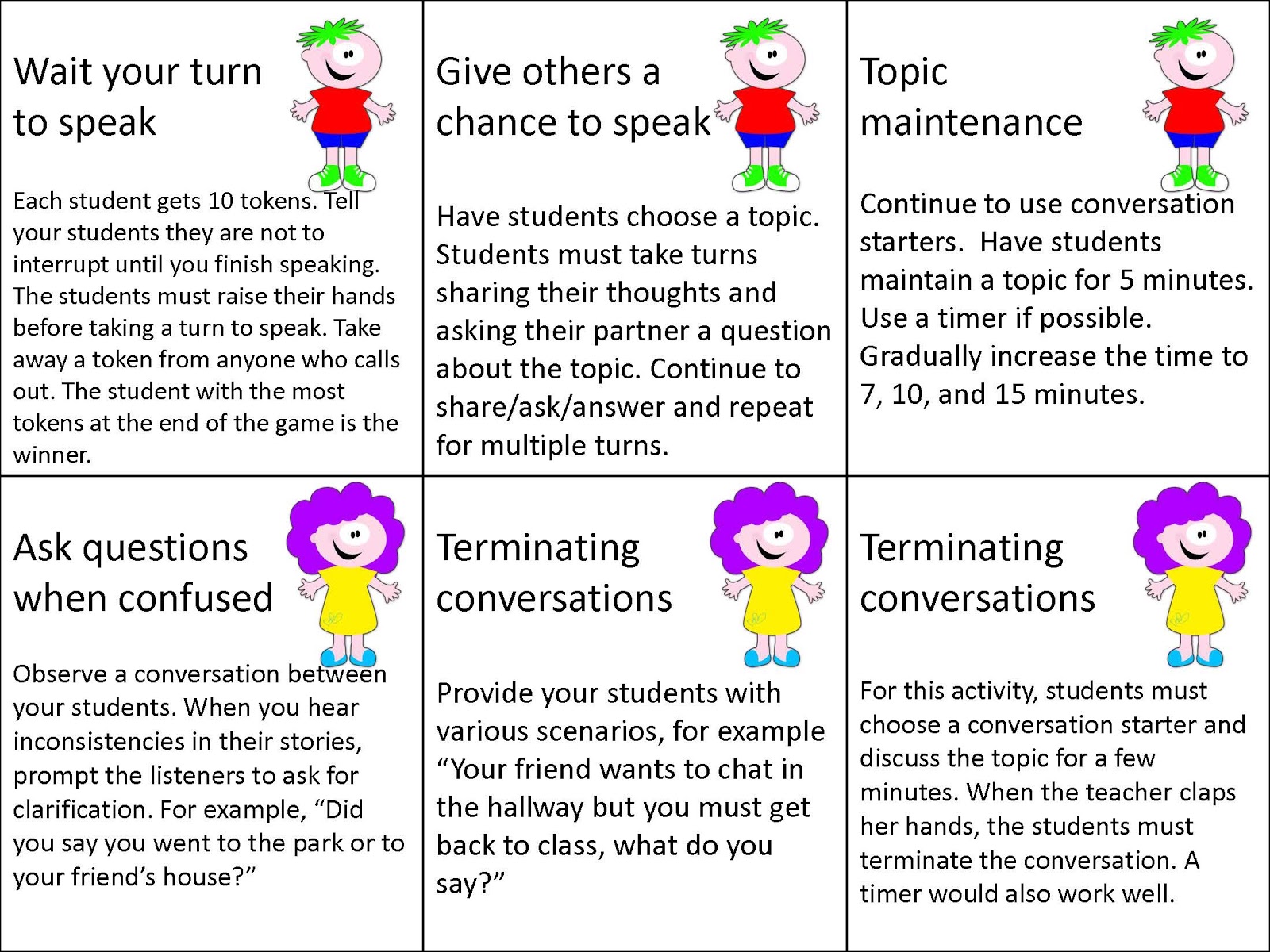
Intervention Programs for Pragmatic Language Disorders
Intervention programs for pragmatic language disorders aim to improve individuals’ ability to use language effectively in social situations. Principles and techniques used include:
- Explicit instruction:Teaching specific pragmatic rules and strategies.
- Modeling:Providing demonstrations of appropriate pragmatic behavior.
- Social skills training:Practicing social interactions in controlled environments.
- Role-playing:Enacting different social scenarios to develop pragmatic skills.
- Feedback:Providing constructive criticism and guidance on pragmatic performance.
Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
Research-supported intervention strategies for pragmatic language disorders include:
- Peer-mediated interventions:Involving peers in language-based activities to promote social interactions and communication.
- Technology-assisted interventions:Using apps and software to provide interactive and engaging learning experiences.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy:Helping individuals understand and modify their thoughts and behaviors related to pragmatic language use.
Cross-Cultural Considerations in Pragmatic Language
/Pragmatics-5900e0fc3df78ca1590318b2.jpg)
Pragmatic language use is heavily influenced by culture, which shapes the way individuals communicate and interact with others. Understanding cultural differences in pragmatic language is crucial for effective cross-cultural communication and avoiding misunderstandings.
Cultural norms and values can significantly impact the interpretation and production of pragmatic language. For example, in some cultures, direct speech is considered appropriate, while in others, indirect or polite language is preferred. Differences in nonverbal communication, such as eye contact, gestures, and facial expressions, can also lead to misinterpretations.
Cross-Cultural Misunderstandings
Cross-cultural misunderstandings can arise due to differences in pragmatic language conventions. For instance, in some cultures, it is considered impolite to interrupt a speaker, while in others, interruptions are seen as a sign of engagement. Similarly, the use of humor can vary across cultures, with some cultures finding certain types of humor offensive or inappropriate.
By being aware of cultural differences in pragmatic language use, individuals can avoid misinterpretations and communicate more effectively across cultures.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, pragmatic language plays a pivotal role in our ability to communicate effectively and navigate social situations. By understanding its complexities and nuances, we can enhance our communication skills, build stronger relationships, and create a more inclusive and harmonious society.
Q&A
What is the significance of pragmatic language?
Pragmatic language is essential for effective communication as it allows us to convey our intentions, understand the nuances of social interactions, and adapt our language to different contexts.
How does pragmatic language develop?
Pragmatic language skills develop gradually throughout childhood and adolescence, influenced by factors such as exposure to language, social interactions, and cultural norms.
What are common pragmatic language disorders?
Pragmatic language disorders include autism spectrum disorder, social communication disorder, and specific language impairment, characterized by difficulties with understanding and using pragmatic language.